Navigating the AI Transformation Tightrope: Balancing Innovation, Regulation, and Human Capital
The artificial intelligence landscape in late 2025 presents a complex picture of immense opportunity tempered by significant operational challenges....
6 min read
 Peter Vogel
:
June 23, 2025
Peter Vogel
:
June 23, 2025

The AI landscape is changing at an accelerating pace, bringing both exciting advancements and complex challenges. As AI implementation becomes more widespread, organisations are grappling with evolving ethical considerations, the need for practical AI fluency, and the strategic importance of clear communication. The increasing pressure to adopt AI responsibly and effectively necessitates a proactive and adaptable approach from business leaders across all sectors.
This week, we cut through the noise to deliver actionable insights on AI's evolving ethical landscape, the practical value of AI Fluency, and the often-overlooked power of clear description. We aim to equip you with the knowledge to navigate these shifts and strategically implement AI for tangible business impact. This article is for Operations/Technology Executives, Marketing Leaders, Growth-Focused CEOs, Sales Directors, Customer Service Leaders, and HR/Training Leaders seeking practical guidance on AI adoption.

Ethical AI is no longer just a ""nice-to-have"" but a critical factor for brand reputation, regulatory compliance, and long-term sustainability. The increasing financial and legal risks associated with biased or unethical AI deployments are becoming impossible to ignore. The EU AI Act, with its significant financial penalties for bias, serves as a stark reminder of this reality [TechCrunch, 2025]. The NIST AI Risk Management Framework 2.0, featuring a dynamic bias scoring system, provides a structured approach to managing these risks, but its implementation requires dedicated effort [NIST.gov, 2025]. Moreover, a Stanford study recently revealed that LLMs amplify cultural stereotypes, further highlighting the pervasive nature of bias in AI systems [Stanford HAI, 2025].
The need for dedicated AI ethics officers, bias auditing processes, and comprehensive training programmes is becoming increasingly apparent, with 78% of Fortune 500 companies now employing dedicated ethics officers [Deloitte, 2025]. Forward-thinking organisations are recognising the opportunity to build a competitive advantage through ethical AI practices, attracting both talent and customers who value responsible innovation, as companies using bias-mitigation tools saw 29% higher customer satisfaction scores [Gartner, 2025]. However, detecting subtle biases, fostering diverse teams, and balancing innovation with ethical guardrails present significant implementation challenges.

Description is a core AI fluency skill, crucial for driving efficiency, improving output quality, and ensuring ethical use. It's the ability to clearly articulate AI systems’ functions, limitations, and data sources, enabling effective human-AI interaction. Helium42's view is that ""description"" is essential for responsible AI adoption, highlighting its role in effective human-AI collaboration. An MIT study underscores this point, demonstrating that ""descriptive transparency"" can reduce AI errors [MIT Technology Review, 2025]. Organisations with strong description protocols saw a 40% reduction in AI errors compared to peers [MIT Technology Review, 2025].
Practical applications include using clear prompts to achieve desired outputs from content creation tools, ensuring that AI systems are used effectively and ethically. Organisations need to train employees on effective prompting techniques, develop clear communication strategies for AI interactions, and establish guidelines for describing AI systems and their limitations. However, defining clear and concise prompts, iteratively refining them, and adapting description strategies to different AI models present ongoing challenges.

As AI capabilities increase, ensuring predictable and reliable performance becomes a growing challenge. Despite advancements, understanding and controlling AI reasoning processes remain complex. Apple's research into Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) indicates current models struggle with logical step-by-step problem-solving, failing at complex tasks even when provided algorithms [Apple LRM Research, 2025]. The ability to guide AI effectively is not always guaranteed, even when models demonstrate high-level performance in certain areas. This unpredictability underscores the need for robust monitoring and control mechanisms.
Human oversight remains critical for ensuring responsible and effective AI deployment. Organisations must implement robust feedback systems to track AI performance and identify potential anomalies. The challenge lies in aligning AI with human values and intentions, requiring ongoing evaluation and preparation for unexpected outcomes.

The creative landscape is undergoing a rapid transformation driven by the rise of AI-generated content. This shift is redefining artistic value and taste, impacting creative industries and necessitating adaptation from creative professionals [Report 5 Executive Summary, 2025]. The emergence of AI-generated advertising at scale, exemplified by examples like the Kalshi ad created by PJ Ace using generative video tools in days, demonstrates this transformation [AI Daily Brief Summary, 2025]. Debates around licensing and copyright litigation, such as the Disney vs. Midjourney case, highlight the legal complexities of AI-generated content [Disney/Universal Lawsuit, 2024].
Creative professionals must adapt to AI tools, embrace new workflows, and focus on developing unique skills and expertise. Understanding copyright and intellectual property issues is crucial for navigating this evolving landscape. The democratisation of content creation through AI [Report 5 Executive Summary, 2025] presents both opportunities and challenges for creative industries.

Recursive self-improvement is a transformative concept with the potential to unlock unprecedented levels of AI performance and autonomy [Recursive Improvement Video Summary, 2025]. This process, where AI systems improve themselves by generating their own training data and refining their algorithms, is redefining AI's potential. An MIT paper on Self-Adapting Language Models (SEAL) showcases this capability, demonstrating how AI can autonomously generate its own training data and apply weight updates [MIT, 2025]. This self-evolving capability signals a shift in the market and the potential for new software optimisation techniques.
Organisations must develop new evaluation and monitoring frameworks to track the performance of self-improving AI systems. Ethical considerations and safety protocols are paramount as AI systems gain the ability to evolve independently. The difficulty of controlling and aligning self-improving AI systems, along with the potential for unintended consequences, requires robust monitoring and evaluation mechanisms.
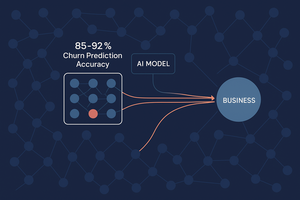
The artificial intelligence landscape in late 2025 presents a complex picture of immense opportunity tempered by significant operational challenges....

The discourse surrounding artificial intelligence is maturing. Across boardrooms and operational teams, the conversation has decisively shifted from...
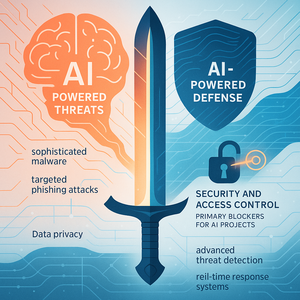
The artificial intelligence landscape is no longer a distant frontier; it's rapidly reshaping the present, demanding a strategic response from...